|
|
|
Subscribe INTRODUCTION
As such, Green Chemistry is a step towards sustainability. Its application means a chemistry whose products and processes seek to achieve a balance that is environmentally healthy, socially viable, economically profitable, energy desirable and ethically acceptable. Green Chemistry is applied throughout the life cycle of a chemical, including not only its design and manufacture, but also its use and ultimate disposal. "Green chemical" is a common term used in Green Chemistry and it refers to any substance that provides higher performance and functionality compared to non-green chemicals, while being more environmentally benign throughout its entire life cycle. Examples of its application can be found in many fields (pharmaceutical, cosmetic, chemical, agricultural, etc.), especially in the design of production processes and the use of green chemicals in consumer products. Inkemia IUCT group is a leader in this area. For 20 years, it has been designing, developing and commercializing new Green Chemistry products and processes. Nowadays Inkemia has an extensive library of green chemicals, and has helped many companies at a national and international level to improve processes, products and formulations according to the principles of Green Chemistry. PRINCIPLES OF GREEN CHEMISTRY The 12 basic principles of Green Chemistry were developed by Paul Anastas and John Warner in their book Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice in the late 90s. These principles link the design of chemical products and processes with their impact on human health and environment. 1. Prevention: It is better to prevent waste than to treat or clean up waste after it has been created. 2. Atom Economy: Synthetic methods should be designed to maximize the incorporation of all materials used in the process into the final product. 3. Less Hazardous Chemical Syntheses: Wherever practicable, synthetic methods should be designed to use and generate substances that possess little or no toxicity to human health and the environment. 4. Designing Safer Chemicals: Chemical products should be designed to carry out their desired function while minimizing their toxicity. 5. Safer Solvents and Auxiliaries: The use of auxiliary substances (e.g., solvents, separation agents, etc.) should be made unnecessary wherever possible and innocuous when used. 6. Design for Energy Efficiency: Energy requirements of chemical processes should be recognized for their environmental and economic impacts and should be minimized. If possible, synthetic methods should be conducted at ambient temperature and pressure. 7. Use of Renewable Feedstocks: A raw material or feedstock should be renewable rather than depleting whenever technically and economically practicable. 8. Reduce Derivatives: Unnecessary derivatization (use of blocking groups, protection/deprotection, temporary modification of physical/chemical processes) should be minimized or avoided if possible, because such steps require additional reagents and can generate waste. 9. Catalysis: Catalytic reagents (as selective as possible) are superior to stoichiometric reagents. 10. Design for Degradation: Chemical products should be designed so that at the end of their function they break down into innocuous degradation products and do not persist in the environment. 11. Real-time analysis for Pollution Prevention: Analytical methodologies need to be further developed to allow for real-time, in-process monitoring and control prior to the formation of hazardous substances. 12. Inherently Safer Chemistry for Accident Prevention: Substances and the form of a substance used in a chemical process should be chosen to minimize the potential for chemical accidents, including releases, explosions, and fires. Green Chemistry is a discipline that applies to all areas of chemistry. Its ultimate goal is for the 12 principles to be incorporated as part of everyday chemistry.
EXAMPLES OF GREEN CHEMISTRY APPLICATION In the manufacture of electronic chips: the use of supercritical fluids (SCF) has contributed to a significant reduction in the consumption of chemicals, energy and water in the process. In the active ingredients synthesis for the Pharmaceutical Industry: there are numerous applications for biocatalysis and the removal or replacement of standard solvents by green solvents:
In the development of biodegradable plastic – several companies have worked in the development of these kinds of plastic from renewable raw materials, such as cornstarch or yucca starch. Additionally, many examples exist in the paint and coatings industry for replacing resins and VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds) with less toxic alternatives that produce less waste. In addition, among the numerous examples of the application of Green Chemistry there’s the evolution of chemistry in pest-control products, from organochlorine compounds and its associated bioaccumulation and high persistence to the latest pest-control products that maintain their efficacy against pests and are quickly naturally degraded to safe products, preventing them from having a negative impact on the environment and humans. Other examples of Green Chemistry advancements can be found in the biofuels industry, ecological dry cleaning and sterilization. In short, through molecular design and innovation, Green Chemistry has become a powerful tool that contributes to:
1. the reduction of chemical hazards related to the use and manufacture of chemical products;
INKEMIA IUCT GROUP AND ITS KNOWLEDGE IN GREEN CHEMISTRY AT YOUR SERVICE In 1997 Inkemia IUCT group created the first program on Green Chemistry in Spain. Three years later, it became part of the International Network of the Green Chemistry Institute as the Spanish delegation, and in 2003 joined its Management Board. That same year, Inkemia IUCT group was also a cofounder of the Spanish Network of Sustainable Chemistry. In 2004 it established the industrial European consortium SOLVSAFE, and in 2005 Inkemia IUCT group was appointed a member of the Spanish Network of Sustainable Chemistry’s Management Board. Between 1999 and 2013, Inkemia IUCT group organized the Green Chemistry conference, and since its constitution has participated in several public-private consortia aimed at the execution of research projects following the principles of Green Chemistry.
Products developed by IUCT:
Throughout this time, Inkemia has collaborated with industry and, among other successes, achieved the following:
In 2016 Inkemia IUCT group demonstrated its firm commitment to Green Chemistry with the creation of its first subsidiary in the USA specialized in Green Chemistry. Inkemia Green Chemicals is honoured to have Paul Anastas, considered the father of Green Chemistry, as President of its Scientific Board.
How can InKemia and Green Chemistry assist your company? Inkemia IUCT group has one of the widest libraries of functional green products. Its diversity has been carefully designed to meet the technical specifications of the different applications required in various sectors. Among the numerous solutions that we can offer from a Green Chemistry perspective are the following:
Chemical processes optimization/Syntheses redesign:
Industrial Biotechnology
Contamination prevention
This breadth of knowledge and development makes Inkemia IUCT group an ideal partner in your search for green solutions that meet your needs. For more information contact This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
|
 English
English  Portuguese
Portuguese  Català
Català  Español
Español 
 Green Chemistry is the design of chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the generation and/or use of hazardous substances.
Green Chemistry is the design of chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the generation and/or use of hazardous substances.

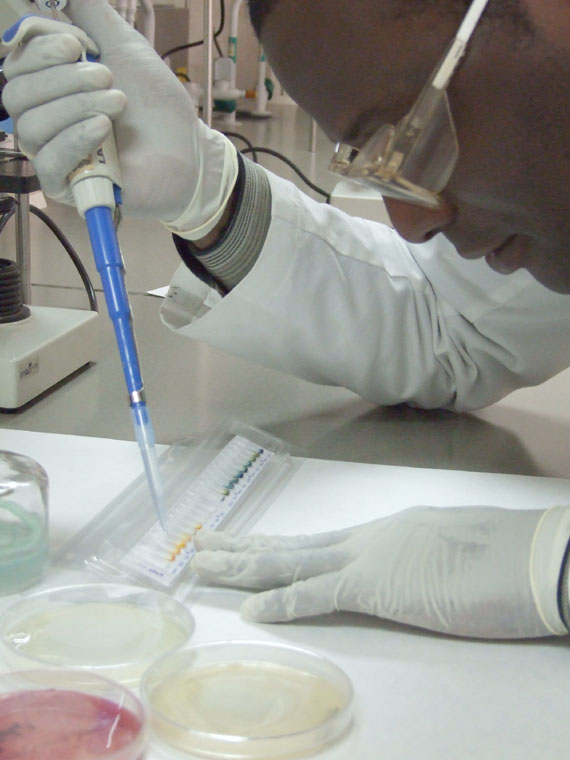 Formulation Improvement of cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, food supplements, etc.
Formulation Improvement of cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, food supplements, etc.