|
|
||
|
Today we are introducing our newsletter with one goal: building a communication channel with you. A communication line that goes in both directions, approaching you to our knowledge and activity, and bringing us closer to your interests. We hope that you will find them interesting and invite you to send us suggestions about future contents to This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.. Our first publication deals with the import of pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. Future editions will focus on other subjects such as NMR and its applications, ENAC certification, biocatalysis and other issues related to the life science industry. IMPORTING INTO THE EU PHARMACEUTICALS AND COSMETICS MANUFACTURED IN THIRD COUNTRIES According to current EU regulations, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, manufactured in third countries and imported into the EU, have to be certified for its quality and compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices by an authorized importer with a qualified team. You will find a review of the current regulations in the following sections. If you have interest in importing such products Inkemia may help you in all or part of the process.
EUROPEAN PROVISIONS FOR IMPORTING PHARMACEUTICALS FROM THIRD COUNTRIES
Obligations related to batch certification are listed in Annex 16 and include:
However, the publication of a new annex to the rules of GMP dedicated to import of drugs (Annex 21) is expected this year. In this text the most relevant requirements, from the point of view of GMP, for importers and the different entities involved in import activities will be highlighted.
As a consequence, IUCT widens its range of services by adding quality control, batch certification and release in Europe of pharmaceutical products manufactured in third countries. Additionally, in an effort to provide a global service, IUCT also offers support in other activities related to the import and marketing of pharmaceutical products in the European Union. Within the range of services IUCT offers you can find: preparation and submission of dossiers in the European countries of your interest, support in getting GMP certification of the manufacturer's facilities, transport & customs and pharmacovigilance services, audit services, among others.
Cosmetics within European countries are regulated by Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 since 11th July 2013, meaning that its provisions will be of application in all Member States, without being subject to potential alterations when translated into national legislations. Summarizing, the main requirements that a cosmetic product has to comply with are:
In Spain, the cosmetics import activities are subject to a notification procedure based on a responsible declaration, governed by Article 71a of Law 30/1992 of 26 November. This responsible statement must be submitted to the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS). That submission will allow the start of activities, without prejudice to subsequent verification by the AEMPS, through documentary verification and, where appropriate, inspection of the elements and circumstances revealed in the declaration of responsibility. In short, the obligations for a importer of cosmetics products detailed in the responsible statement are:
INKEMIA AT YOUR SERVICE TO HELP YOU IMPORTING COSMETICS TO THE EUROPEAN UNION Inkemia can help you when importing cosmetics manufactured in third countries into the EU in different ways, such as:
|
Newsletter July 2016. RMN
|
|
|
Nowadays, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR) has become a very relevant analytical technique with a wide number of applications in many disciplines of scientific research and medicine plus in various industries (pharmaceuticals, food, agrochemicals, etc). The developments in both methodology and instrumentation in the past two decades, has made of NMR one of the most sophisticated, powerful and versatile techniques for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of complex mixtures and natural products.
INTRODUCTION
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is based on the use of absorption and re-emission of electromagnetic radiation occuring when the nuclei of certain atoms are immersed in a static magnetic field and then exposed to a second oscillating magnetic field.
Among those applications listed above, quantitative analysis using NMR and its use in pharmaceuticals, food and agrochemicals are reviewed in the following sections.
Quantitative NMR spectroscopy (qNMR) is one of the most informative methods for the identification, authentication, and detailed analysis of the structures of any organic compound and their mixtures. It is described in the European Pharmacopoeia as one of the suitable analytical techniques to be used for qualitative and quantitative purposes. The main advantages of the NMR are:
NMR spectroscopy has evolved as one of the most powerful analytical techniques for the pharmaceutical industry. European Pharmacopoeia and US Pharmacopoeia (USP) have recognized its value and have developed general chapters describing the equipment, techniques, as well as the quantitative and qualitative methodology to be used. Both Pharmacopeias also have official monographs with tests based on NMR techniques, particularly for more complex natural and biological substances. In general NMR is used for identification and assay of active substances or for related substances and other impurity tests. Among the main applications of NMR analysis are:
NMR APPLICATIONS IN FOOD AND AGRICULTURE During the last two decades, the use of NMR spectroscopy for the characterization and analysis of food and agrochemical materials has flourished, and this trend continues to increase today. Some examples are described below.
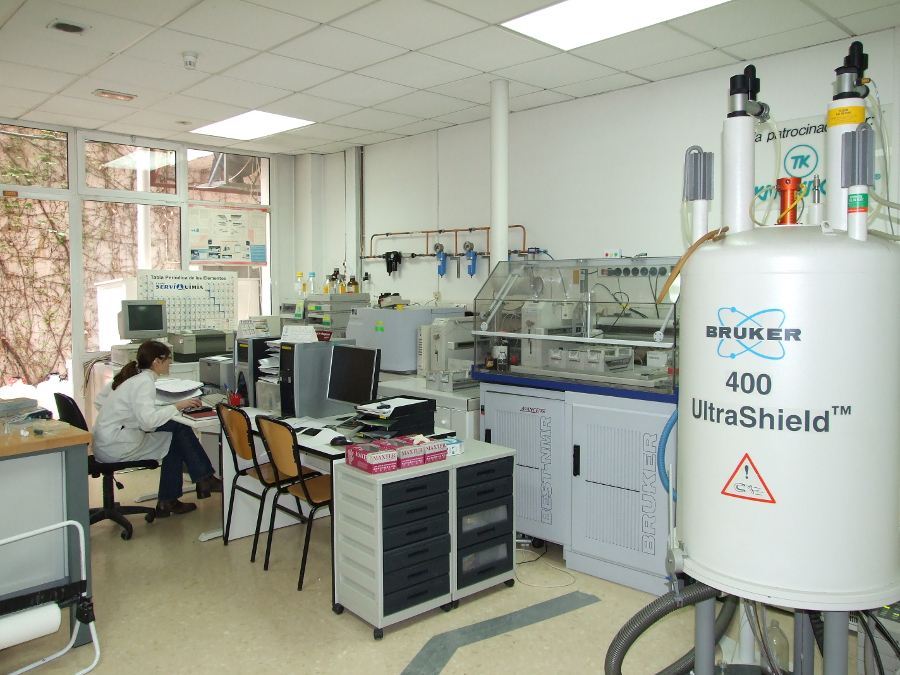
INKEMIA EXPERTISE IN NMR ANALYSIS
InKemia has a large expertise and know-how in the application of NMR techniques to support chemical and pharmaceutical industry in both, qualitative and quantitative analysis.
|
 English
English  Portuguese
Portuguese  Català
Català  Español
Español 




