|
Subscribe
Nowadays, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR) has become a very relevant analytical technique with a wide number of applications in many disciplines of scientific research and medicine plus in various industries (pharmaceuticals, food, agrochemicals, etc). The developments in both methodology and instrumentation in the past two decades, has made of NMR one of the most sophisticated, powerful and versatile techniques for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of complex mixtures and natural products.
Inkemia has been working on this field over the last ten years. The company currently has a qualified equipment working within a Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) environment and it is able to give various solutions to industries of the lifescience sector.
In this newsletter you will find a brief overwiew on the advantages of NMR and its various applications.
INTRODUCTION
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is based on the use of absorption and re-emission of electromagnetic radiation occuring when the nuclei of certain atoms are immersed in a static magnetic field and then exposed to a second oscillating magnetic field.
Since NMR is sensitive to compounds bearing 1H or 13C, 19F, 15N, 31P, it can be regarded as a quasi-universal detector of organic compounds.
No other analytical technique provides such qualitative and quantitative information in a single analysis, without using external standards or isolation of the different components contained in the sample.
NMR is a robust analytical technique of non-destructive nature which provides solutions to industries allowing easy and simple sample preparation and method development.
The main applications of NMR analysis are:
-
Structural elucidation of organic molecules.
-
Deformulation of products in order to identify individual components of a formulated product.
-
Identification of impurities and unknown compounds in complex samples.
-
Quantification of mixture components.
-
Quality control of bulk chemicals, pharmaceutical products, natural products, food and nutraceuticals.
-
Raw materials fingerprinting.
-
Kinetic and temperature studies of reaction mixtures.
-
Determination of enantiomeric.
Among those applications listed above, quantitative analysis using NMR and its use in pharmaceuticals, food and agrochemicals are reviewed in the following sections.
QUANTITATIVE NMR APPLICATIONS
Quantitative NMR spectroscopy (qNMR) is one of the most informative methods for the identification, authentication, and detailed analysis of the structures of any organic compound and their mixtures. It is described in the European Pharmacopoeia as one of the suitable analytical techniques to be used for qualitative and quantitative purposes. The main advantages of the NMR are:
-
Integrated NMR intensities of the signals are directly proportional to the number of atoms of the molecular group responsible for that signal.
-
Therefore, complicated samples can be analyzed without using external standards and references, which is unavoidable in chromatographic, mass spectrometric, photometric, and other analytical methods used.
-
Requirement of determining response factors can be avoided since protons are detected with the same sensitivity, regardless of the chemical environment.
-
Besides, there is also a linear relationship between the integrated intensities of the resonances from separate components in the spectrum and their contents in the studied substances so multiple components can be quantified in a complex samplein one experiment without previous separation.
NMR APPLICATIONS IN THE PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY
NMR spectroscopy has evolved as one of the most powerful analytical techniques for the pharmaceutical industry. European Pharmacopoeia and US Pharmacopoeia (USP) have recognized its value and have developed general chapters describing the equipment, techniques, as well as the quantitative and qualitative methodology to be used. Both Pharmacopeias also have official monographs with tests based on NMR techniques, particularly for more complex natural and biological substances. In general NMR is used for identification and assay of active substances or for related substances and other impurity tests. Among the main applications of NMR analysis are:
-
Quantitative NMR spectroscopy (qNMR): Due to equal response for any dissolved compound, NMR spectroscopy is an excellent technique for quantification of any substance.
-
Some examples of qNMR include determination of the purity of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) as well as quantification of active ingredients, excipients and impurities in pharmaceutical products. Residual solvents, isomers, diastereomers and enantiomeric excess can also be determined.
-
Quantitative NMR techniques can be advantageously used as an alternative to conventional high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) when impurity standards are not available, as in early stages of drug development.
-
Impurity profile studies: NMR spectroscopy has evolved into an irreplaceable approach for pharmaceutical quality assessment, currently playing a critical role in unequivocal structure identification as well as structural confirmation.
-
NMR analysis can provide detailed information about molecular structures and helps to confirm and establish the identity of pharmaceutical substances and impurities.
-
The capability of the NMR analysis to perform concurrent identification and quantification of impurities turns qHNMR into an unique analytical tool for the pharmaceutical industry.
-
Drug discovery research: NMR is being used widely in the area of drug design. Such studies usually aim to obtatin:
-
The structure of the drug molecule, its receptor bound conformation as well as its dynamics at the receptor site.
-
The structure of the receptor and its complex with the drug, which provides the information on the binding site and functional group interaction participating in the ligand recognition and its binding.
NMR APPLICATIONS IN FOOD AND AGRICULTURE
During the last two decades, the use of NMR spectroscopy for the characterization and analysis of food and agrochemical materials has flourished, and this trend continues to increase today.
Some examples are described below.
-
Wine analysis for detection of variety, geographical origin and adulterations, which allows the creation of a fingerprint database of the different wines.
-
Analysis of olive oil, multinuclear (1H, 13C, 31P) NMR spectroscopy is a valuable tool for the determination of several bioactive compounds, its evaluation and authentication purposes.
-
Honey analysis for the detection of exogenous sugars.
-
Coffee analysis: Colombian coffees authentification using 1H-NMR fingerprints.
INKEMIA EXPERTISE IN NMR ANALYSIS
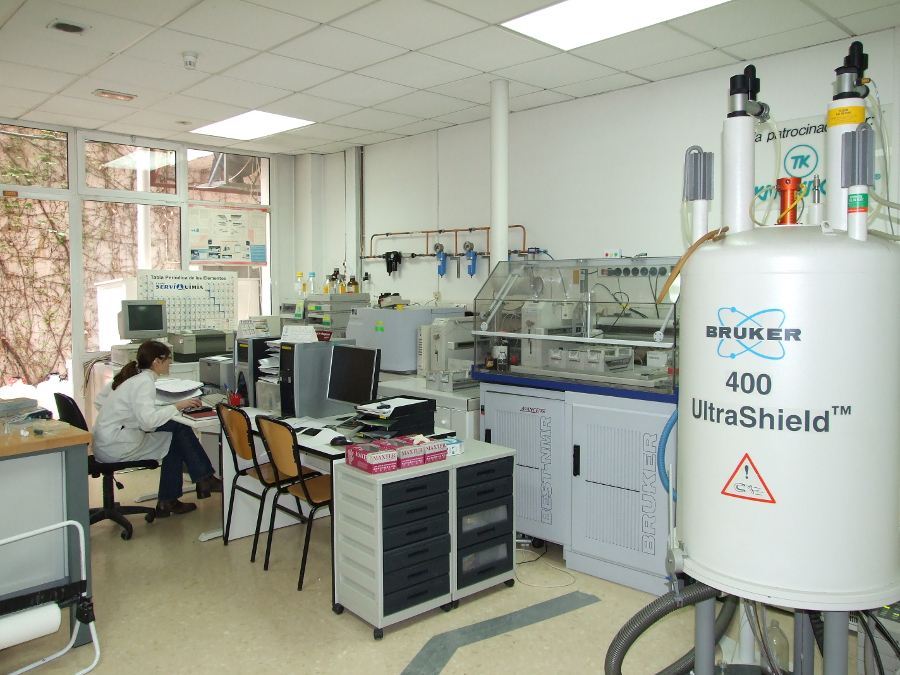
InKemia has a large expertise and know-how in the application of NMR techniques to support chemical and pharmaceutical industry in both, qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Inkemia offers high resolution NMR analysis, which includes a qualified 400 MHz spectrometer working in a Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) environment. That means all data generated can be used to support regulatory submissions and also can support pharmaceutical development from early stage through to post-approval.
The main services offered are:
-
Qualitative NMR analysis for structural elucidation purposes:
-
Identification of unknown substances.
-
Determination of reaction intermediates.
-
Identification of impurity profile and unknowns in APIs or formulated products.
-
Development of routine qualitative and quantitative analysis for screening of a large number of related samples.
-
The development of qualitative and quantitative NMR validated methods, ensuring the right approaches are applied to the client specific requirements.
-
Chiral purity determination.


|
 English
English  Portuguese
Portuguese  Català
Català  Español
Español 

